Essential Terminology Explained
Are you fascinated by the mesmerizing world of surface pattern design but find yourself puzzled by the terminology used in this creative field? In that case, keep reading and unravel the most commonly used terms within the surface pattern design industry.
The Basics of Surface Pattern Design
1) Pattern
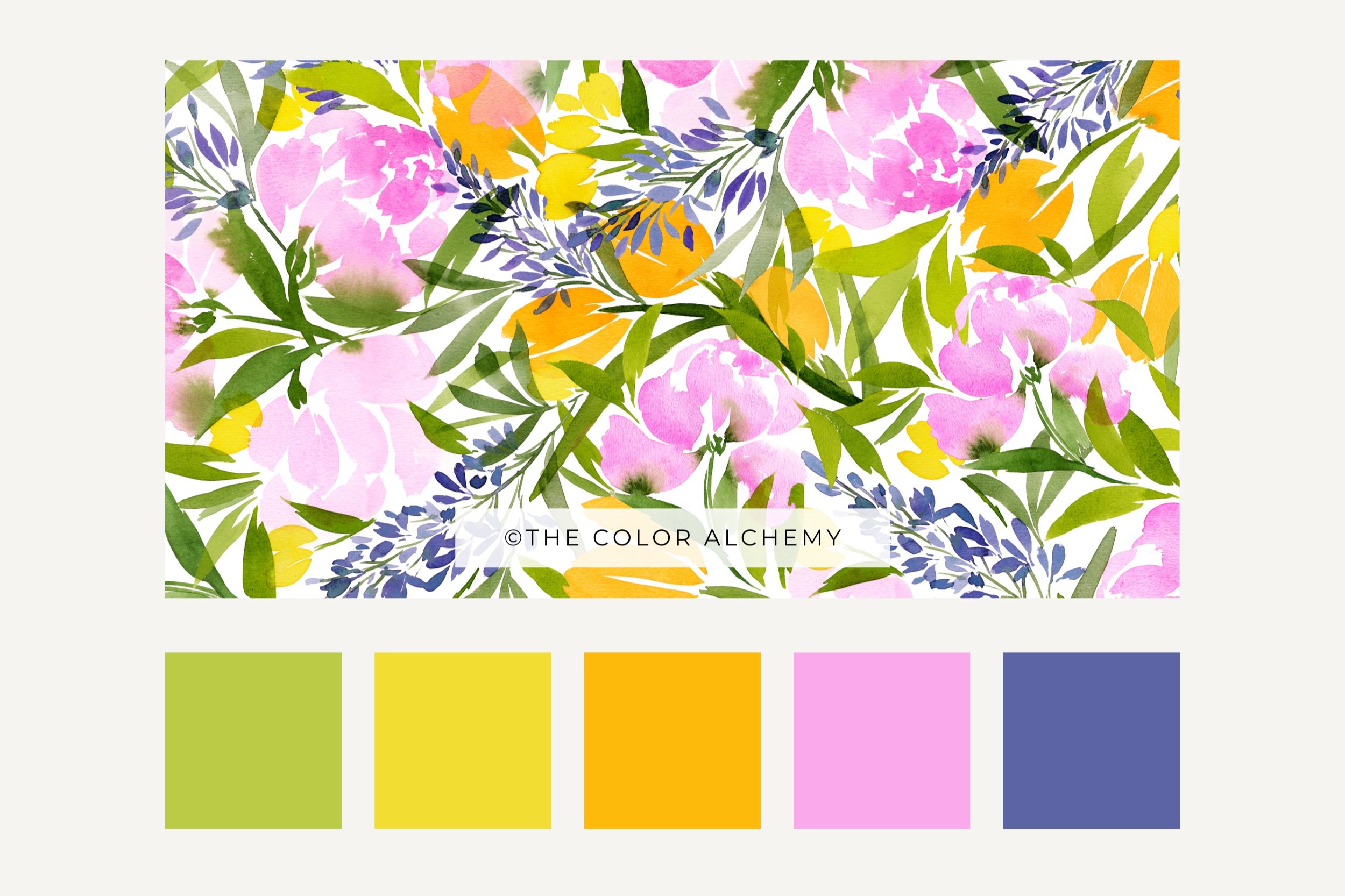
A pattern is a repetitive arrangement of elements or motifs that creates a visual structure or design. It is composed of recurring shapes, colors, or motifs arranged in a systematic manner. Patterns can be simple or complex, abstract or representational, and they often evoke a sense of rhythm, harmony, and visual interest.
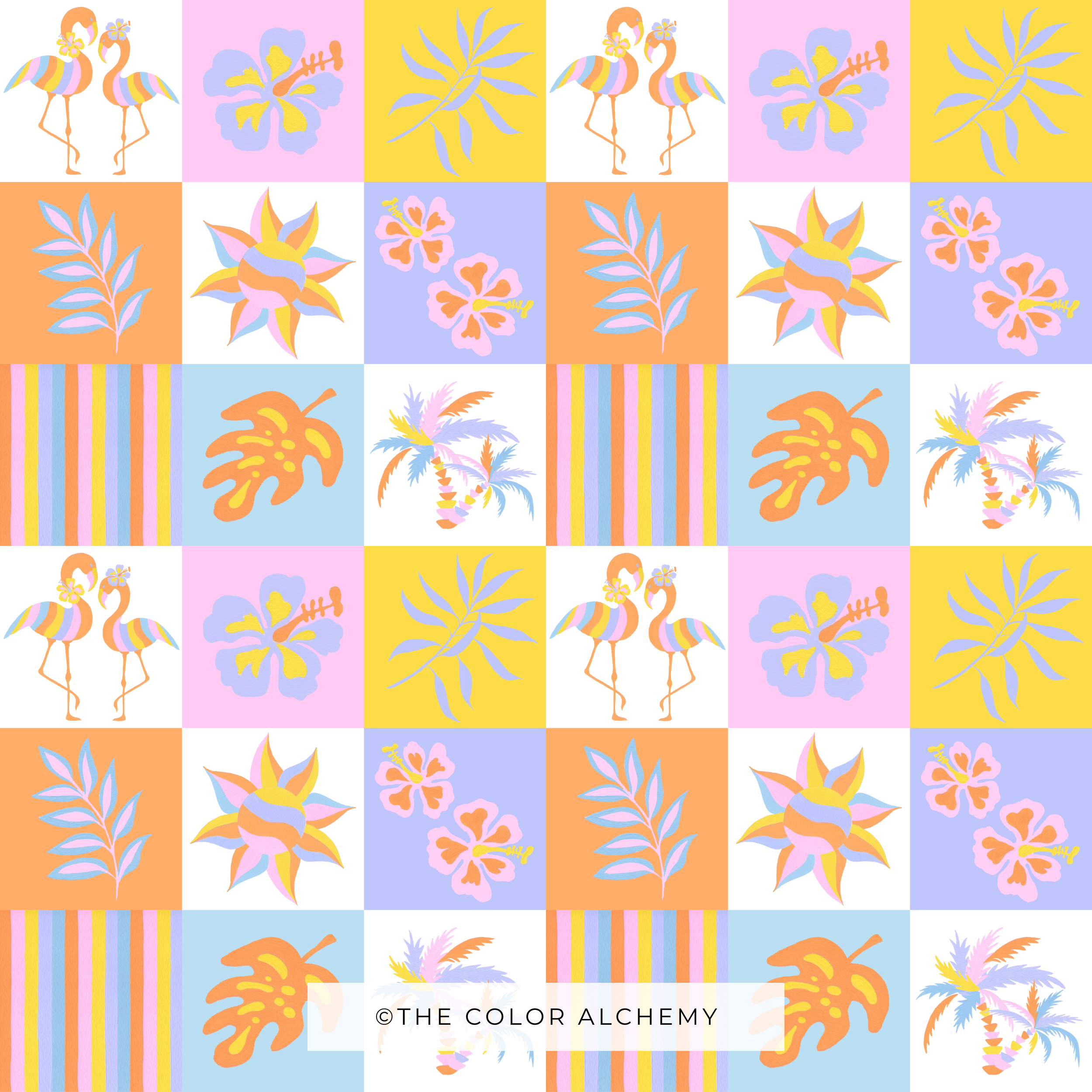
IN THE TREES Pattern collection by THE COLOR ALCHEMY
2) Pattern Collection
A pattern collection is a carefully chosen group of designs with a common theme or style. Important aspects of creating a collection include deciding on a main theme, offering variety in designs, keeping colors consistent, and being aware of seasonal or trendy influences.
3) Hero Pattern
The term "hero pattern" refers to a key or standout pattern within a collection or design portfolio. This pattern is often the focal point or centrepiece of the overall design, commanding attention and serving as a defining element of the collection. A hero pattern is typically chosen for its visual impact, unique characteristics, or ability to represent the essence of the collection's theme or aesthetic.
4) Motif
A motif refers to a recurring element or design feature within a pattern. It can be a simple shape, symbol, or more complex imagery that repeats throughout the design. Motifs play a crucial role in creating cohesion and visual interest within a pattern, adding rhythm and harmony to the overall composition.
5) Tile
A tile is a single unit of the pattern that can be repeated seamlessly to cover a surface. Think of it as a building block that can be replicated in a grid-like fashion to create a continuous pattern. Tiles are designed to fit together seamlessly, ensuring that the pattern repeats without visible breaks or gaps.
6) Grid
A grid is a framework of intersecting lines used to organize and align elements within a pattern. It serves as a guide for placing motifs and arranging tiles in a systematic manner. Designers use grids to ensure precision and consistency in their patterns, helping to maintain symmetry and balance across the surface.
7) Basic Repeat
The simplest form of repeat pattern is the straight repeat, where the pattern elements are aligned straight across and down the surface without shifting. Straight repeats are easy to create and are suitable for patterns with regular motifs and simple compositions.
8) Half-Drop and Brick Repeat
For more dynamic and visually interesting designs, designers often employ half-drop and brick repeats. In a half-drop repeat, the design is shifted halfway down or across from the previous row or column, creating a staggered effect. Brick repeats, on the other hand, involve shifting the design half the width of the motif, resulting in a staggered brick-like arrangement. These types of repeats add movement and rhythm to patterns, making them more engaging and visually appealing.
💡 A tip for book
9) Large-Scale vs Small-Scale Patterns
Patterns can vary widely in scale, from large-scale designs with bold, oversized motifs to small-scale patterns with intricate details and delicate motifs. The size of the pattern elements relative to the overall size of the design can dramatically affect a pattern's visual impact and usability. Large-scale patterns make a bold statement and are well-suited for larger surfaces, such as wallpapers or upholstery fabrics. In contrast, small-scale patterns are more subtle and versatile, making them ideal for smaller items like stationery or accessories.
10) implied vs Seamless Repeat
While both implied repeats and seamless repeats aim to create a cohesive and continuous pattern, the distinction lies in their approach and execution. Implied repeats focus on creating the illusion of continuity beyond the visible boundaries of the pattern, while seamless repeats specifically ensure that the pattern can be tiled or repeated seamlessly without any visible seams or interruptions.
Exploring Colors
1) Colorway
A specific combination of colors used in a pattern design. They can evoke different moods or themes, from vibrant and playful to subdued and elegant. A colorway or color palette consists of a carefully curated selection of hues, shades, and tones that harmonize with each other.
2) Hue, Saturation, Brightness and contrast
The three dimensions of color that determine its appearance. Understanding these properties allows designers to manipulate color effectively. Hue refers to the basic color family (e.g., red, blue, green), while saturation describes the intensity or purity of a color. Brightness, also known as value or lightness, determines how light or dark a color appears. Contrast is the degree of difference between colors used in a design.
3) Complementary Colors
Colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel and create contrast when used together. Complementary colors intensify each other when placed side by side, creating vibrant and visually striking combinations.
4) Analogous Colors
Analogous colors are hues that sit next to each other on the color wheel. These colors share similar undertones and often create harmonious color schemes. For example, a grouping of blue, blue-green, and green is considered analogous. Designers frequently use analogous color schemes to create a sense of unity and coherence in their designs. These schemes are pleasing to the eye and evoke a feeling of balance and tranquillity.
5) Monochromatic Colors
Monochromatic colors are all the different shades, tones, and tints of a single hue. In other words, they consist of variations of one color, ranging from its lightest to darkest shades. For instance, a monochromatic palette based on blue might include sky blue, navy blue, and everything in between. Monochromatic color schemes are elegant and sophisticated, offering a cohesive and unified look.
Monochromatic Color Palette
Digital Tools and Techniques
1) Vector Graphics
Vector graphics are digital images composed of geometric shapes defined by mathematical equations, allowing them to be scaled infinitely without losing quality. They are commonly used in surface pattern design for their crisp lines, scalability, and flexibility.
2) Raster Graphics
Raster graphics are digital images composed of a grid of pixels, each containing color information. They are suitable for creating detailed artwork but may lose quality when resized or scaled up.
3) Adobe Illustrator & Photoshop
Adobe Illustrator is a vector graphics editor widely used by designers to create illustrations, logos, icons, and other graphic elements. Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor known for its extensive range of tools and functionalities for editing and manipulating images. While primarily used for photo editing, Photoshop is also utilized in surface pattern design for tasks such as texture creation and digital painting.
4) Mockup
A digital or physical representation of how a design will look when applied to a specific product or surface. Mockups help designers visualize their patterns in context and assess their suitability for different applications, such as clothing, home decor, or packaging.
Wallpaper Mockup by THE COLOR ALCHEMY - Get it FOR FREE HERE!
5) Pixel
A pixel is the smallest unit of a digital image, representing a single point in a raster grid. Each pixel contains color information, collectively forming the image when viewed at a distance.
6) DPI (Dots Per Inch)
DPI, or dots per inch, is a measure of the resolution or quality of a digital image, indicating the number of dots that can be printed in a linear inch. Higher DPI images have more detail and are suitable for printing at larger sizes, ensuring crisp and sharp output.
7) Resolution
Resolution refers to the clarity or sharpness of an image, typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) for digital images or dots per inch (DPI) for printed images. Higher resolution images contain more detail and are capable of producing clearer and more detailed prints.
8) Vectorization
Vectorization is the process of converting raster graphics into vector graphics, typically achieved through tracing or digitization. This process allows designers to preserve the scalability and flexibility of vector graphics while working with raster-based images.
9) Digital Painting
Digital painting involves creating artwork using digital tools such as a graphics tablet or stylus and software like Adobe Photoshop or Procreate. It offers artists a wide range of brushes, textures, and effects, enabling them to create rich and expressive artwork digitally.
10) Layering
Layering is a technique used in digital design where elements are organized into separate layers, allowing for independent editing and manipulation. Designers use layers to build up complex compositions, apply effects, and manage the hierarchy of elements within a design.
Layers of pattern in Photoshop
Congratulations if you made it all the way through! There is surely much more to demystify in the realm of surface pattern design language, but let's agree that for today, it was enough. Hopefully, the next time you face one of these phrases from a fellow artist or a customer, you will be ready to engage confidently in the conversation.
Pin this article for later ✔
NAVIGATE BY CATEGORY
AUTHOR
HI THERE, I'M PETRA! :)
Independent Surface Pattern Designer, Watercolor Enthusiast and Pattern Lover. The creative force behind THE COLOR ALCHEMY🌈🎨🙋🏻♀️